What is Nested Virtualization?
Virtualization has been a game-changer in the world of computing, enabling efficient utilization of resources and improved scalability.
Introduction
Virtualization has been a game-changer in the world of computing, enabling efficient utilization of resources and improved scalability. Microsoft Azure offers a wide range of virtualization capabilities to meet diverse customer needs. Among its powerful features, Nested Virtualization stands out as a cutting-edge technology that allows users to run virtual machines (VMs) within VMs, unlocking a plethora of use cases and expanding the possibilities of cloud computing.
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/nested-virtualization-in-azure/
Understanding Nested Virtualization
Nested Virtualization refers to the ability to run virtual machines inside other virtual machines, creating multiple layers of virtualization. Traditionally, virtualization technologies relied on hardware-level virtualization support, such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V, which was not available within VMs. However, advancements in software-based virtualization have made nested virtualization possible.
Benefits of Azure Nested Virtualization
- Testing and Development – Nested Virtualization is immensely useful for software development and testing scenarios. Developers can create nested environments within Azure VMs, allowing them to test different configurations, deploy complex applications, and evaluate software compatibility without the need for physical hardware.
- Training and Education – Nested Virtualization facilitates training and education by enabling the creation of virtual lab environments. Instructors can build nested environments to simulate real-world scenarios, providing hands-on experiences to students or team members without requiring dedicated physical infrastructure.
- Isolated Environments – Nested Virtualization offers a sandboxed and isolated environment for experimentation. By nesting VMs, users can create separate instances for specific purposes while maintaining overall system integrity. This can be particularly useful for running un-trusted or potentially risky software.
Implementation of Azure Nested Virtualization
To enable Nested Virtualization in Azure, certain requirements must be met:
- Virtual Machine Generation – Nested Virtualization is supported only on Generation 2 virtual machines.
- VM SKU Types – Azure provides a specific list of VM SKU types that support Nested Virtualization. These sizes are specifically optimized for nested workloads.
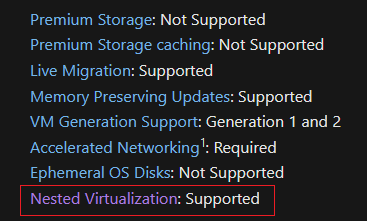
- Operating Systems – The guest operating system running inside the nested VM must also support nested virtualization, such as Windows Server 2016 or later.
Once the requirements are met, enabling Nested Virtualization involves a few configuration steps within the Azure portal or through Azure PowerShell commands. The Azure platform takes care of the underlying virtualization technologies, allowing users to focus on deploying and managing their nested VMs.
Conclusion
Azure Nested Virtualization opens up exciting possibilities within the Azure ecosystem, empowering users to create multi-layered virtual environments and explore various use cases. Whether it’s for testing and development, training and education, or isolated sandboxing, Nested Virtualization provides flexibility and efficiency in utilizing cloud resources. By understanding the technical aspects and implementation requirements, users can leverage Azure Nested Virtualization to drive innovation, streamline workflows, and unlock new opportunities in their cloud computing journey.
Advertisement
Post created using generative AI
